A cache is an area of local memory that holds a copy of frequently accessed data that is otherwise expensive to get or compute. Examples of such data include a result of a query to a database, a disk file or a report.
Here is a simple Java Example which is Threadsafe using HashMap without using Synchronized Collections.
package com.crunchify.tutorials;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
/**
* @author Crunchify.com
*
*/
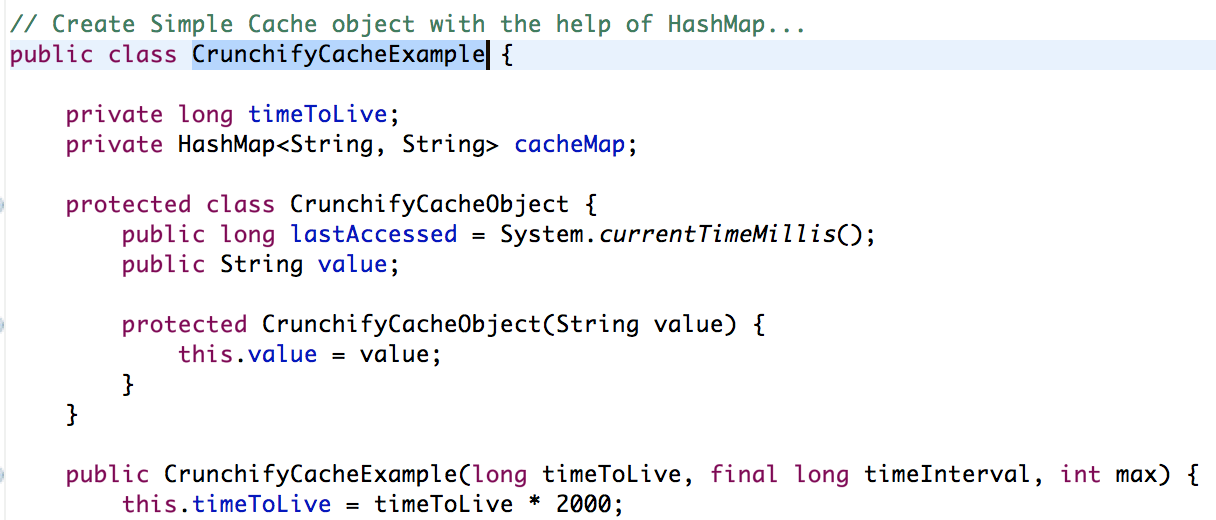
// Create Simple Cache object with the help of HashMap...
public class CrunchifyCacheExample<K, T> {
private long timeToLive;
private HashMap<K, T> cacheMap;
protected class CrunchifyCacheObject {
public long lastAccessed = System.currentTimeMillis();
public String value;
protected CrunchifyCacheObject(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public CrunchifyCacheExample(long timeToLive, final long timeInterval, int max) {
this.timeToLive = timeToLive * 2000;
cacheMap = new HashMap<K, T>(max);
if (timeToLive > 0 && timeInterval > 0) {
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(timeInterval * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
}
}
}
});
t.setDaemon(true);
t.start();
}
}
// PUT method
public void put(K key, T value) {
synchronized (cacheMap) {
cacheMap.put(key, value);
}
}
// GET method
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public T get(K key) {
synchronized (cacheMap) {
CrunchifyCacheObject c = (CrunchifyCacheObject) cacheMap.get(key);
if (c == null)
return null;
else {
c.lastAccessed = System.currentTimeMillis();
return (T) c.value;
}
}
}
// REMOVE method
public void remove(String key) {
synchronized (cacheMap) {
cacheMap.remove(key);
}
}
// Get Cache Objects Size()
public int size() {
synchronized (cacheMap) {
return cacheMap.size();
}
}
// CLEANUP method
public void cleanup() {
long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
ArrayList<String> deleteKey = null;
synchronized (cacheMap) {
Iterator<?> itr = cacheMap.entrySet().iterator();
deleteKey = new ArrayList<String>((cacheMap.size() / 2) + 1);
CrunchifyCacheObject c = null;
while (itr.hasNext()) {
String key = (String) itr.next();
c = (CrunchifyCacheObject) ((Entry<?, ?>) itr).getValue();
if (c != null && (now > (timeToLive + c.lastAccessed))) {
deleteKey.add(key);
}
}
}
for (String key : deleteKey) {
synchronized (cacheMap) {
cacheMap.remove(key);
}
Thread.yield();
}
}
}
Some more Java Examples which you may want to look.
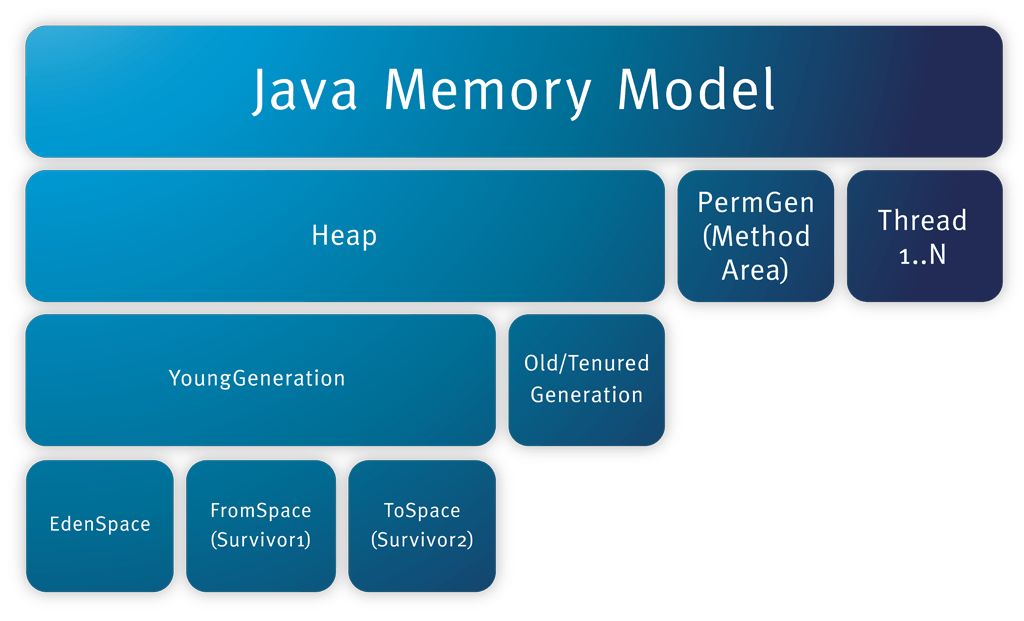
Bonus: Java Memory Model Details: