
If you’re actually building a real production system, then yes, you’d typically just use the stuff in the standard library if what you need is available there. That said, don’t think of this as a pointless exercise.
It’s good to understand how things work, and understanding linked lists is an important step towards understanding more complex data structures, many of which don’t exist in the standard libraries.
There are some differences between the way you’re creating a linked list and the way the Java collections API does it.
The Collections API is trying to adhere to a more complicated interface. Your LinkedList will always have at least one element.
With this kind of setup you’d use null for when you need an empty list. Think of “next” as being “the rest of the list”. In fact many people would call it tail instead of “next”.
Here’s a diagram of a singly LinkedList:
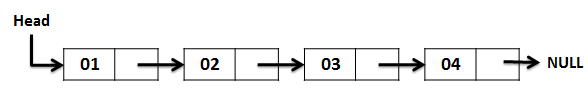
Another must read:
What’s the best way to make a linkedlist in Java from scratch?
Well, here is a simplest implementation of LinkedList Class in Java.
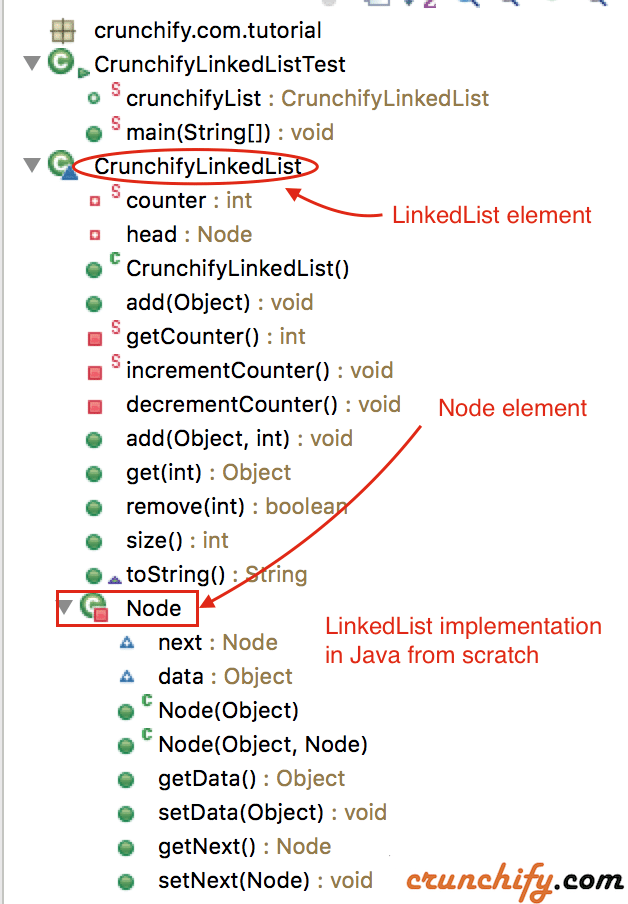
package crunchify.com.tutorial;
/**
* @author Crunchify.com
* version: 1.2
* last updated: 11/10/2015
*/
public class CrunchifyLinkedListTest {
public static CrunchifyLinkedList crunchifyList;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Default constructor - let's put "0" into head element.
crunchifyList = new CrunchifyLinkedList();
// add more elements to LinkedList
crunchifyList.add("1");
crunchifyList.add("2");
crunchifyList.add("3");
crunchifyList.add("4");
crunchifyList.add("5");
/*
* Please note that primitive values can not be added into LinkedList directly. They must be converted to their
* corresponding wrapper class.
*/
System.out.println("Print: crunchifyList: \t\t" + crunchifyList);
System.out.println(".size(): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList.size());
System.out.println(".get(3): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList.get(3) + " (get element at index:3 - list starts from 0)");
System.out.println(".remove(2): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList.remove(2) + " (element removed)");
System.out.println(".get(3): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList.get(3) + " (get element at index:3 - list starts from 0)");
System.out.println(".size(): \t\t\t\t" + crunchifyList.size());
System.out.println("Print again: crunchifyList: \t" + crunchifyList);
}
}
class CrunchifyLinkedList {
private static int counter;
private Node head;
// Default constructor
public CrunchifyLinkedList() {
}
// appends the specified element to the end of this list.
public void add(Object data) {
// Initialize Node only incase of 1st element
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(data);
}
Node crunchifyTemp = new Node(data);
Node crunchifyCurrent = head;
// Let's check for NPE before iterate over crunchifyCurrent
if (crunchifyCurrent != null) {
// starting at the head node, crawl to the end of the list and then add element after last node
while (crunchifyCurrent.getNext() != null) {
crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent.getNext();
}
// the last node's "next" reference set to our new node
crunchifyCurrent.setNext(crunchifyTemp);
}
// increment the number of elements variable
incrementCounter();
}
private static int getCounter() {
return counter;
}
private static void incrementCounter() {
counter++;
}
private void decrementCounter() {
counter--;
}
// inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list
public void add(Object data, int index) {
Node crunchifyTemp = new Node(data);
Node crunchifyCurrent = head;
// Let's check for NPE before iterate over crunchifyCurrent
if (crunchifyCurrent != null) {
// crawl to the requested index or the last element in the list, whichever comes first
for (int i = 0; i < index && crunchifyCurrent.getNext() != null; i++) {
crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent.getNext();
}
}
// set the new node's next-node reference to this node's next-node reference
crunchifyTemp.setNext(crunchifyCurrent.getNext());
// now set this node's next-node reference to the new node
crunchifyCurrent.setNext(crunchifyTemp);
// increment the number of elements variable
incrementCounter();
}
public Object get(int index)
// returns the element at the specified position in this list.
{
// index must be 1 or higher
if (index < 0)
return null;
Node crunchifyCurrent = null;
if (head != null) {
crunchifyCurrent = head.getNext();
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
if (crunchifyCurrent.getNext() == null)
return null;
crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent.getNext();
}
return crunchifyCurrent.getData();
}
return crunchifyCurrent;
}
// removes the element at the specified position in this list.
public boolean remove(int index) {
// if the index is out of range, exit
if (index < 1 || index > size())
return false;
Node crunchifyCurrent = head;
if (head != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
if (crunchifyCurrent.getNext() == null)
return false;
crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent.getNext();
}
crunchifyCurrent.setNext(crunchifyCurrent.getNext().getNext());
// decrement the number of elements variable
decrementCounter();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// returns the number of elements in this list.
public int size() {
return getCounter();
}
public String toString() {
String output = "";
if (head != null) {
Node crunchifyCurrent = head.getNext();
while (crunchifyCurrent != null) {
output += "[" + crunchifyCurrent.getData().toString() + "]";
crunchifyCurrent = crunchifyCurrent.getNext();
}
}
return output;
}
private class Node {
// reference to the next node in the chain, or null if there isn't one.
Node next;
// data carried by this node. could be of any type you need.
Object data;
// Node constructor
public Node(Object dataValue) {
next = null;
data = dataValue;
}
// another Node constructor if we want to specify the node to point to.
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public Node(Object dataValue, Node nextValue) {
next = nextValue;
data = dataValue;
}
// these methods should be self-explanatory
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public void setData(Object dataValue) {
data = dataValue;
}
public Node getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node nextValue) {
next = nextValue;
}
}
}
Few things:
Here we are initialize Node only while adding 1st element.
// Initialize Node only incase of 1st element
if (head == null) {
head = new Node(data);
}
Result:
Print: crunchifyList: [1][2][3][4][5] .size(): 5 .get(3): 4 (get element at index:3 - list starts from 0) .remove(2): true (element removed) .get(3): 5 (get element at index:3 - list starts from 0) .size(): 4 Print again: crunchifyList: [1][2][4][5]
Enhancements to this implementation include making it a double-linked list, adding methods to insert and delete from the middle or end, and by adding get and sort methods as well.
Referenced answer from Stack Overflow by Laurence Gonsalves. You may be interested in list of all Java Tutorials.
