
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format. It is easy for humans to read and write. It is easy for machines to parse and generate. It is based on a subset of the JavaScript Programming Language.
JSON is built on two structures:
- A collection of
name/value pairs. In various languages, this is realized as an object, record, struct, dictionary, hash table, keyed list, or associative array. - An ordered list of values. In most languages, this is realized as an array, vector, list, or sequence.
List of all JSON Tutorials: https://crunchify.com/category/json/
In JSON, they take on these forms:
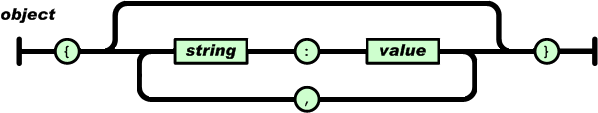
An object is an unordered set of name/value pairs. An object begins with { (left brace) and ends with } (right brace). Each name is followed by : (colon) and the name/value pairs are separated by , (comma).
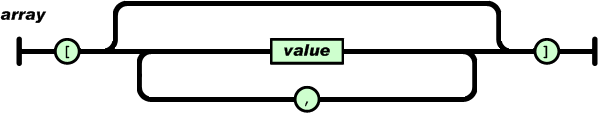
An array is an ordered collection of values. An array begins with [ (left bracket) and ends with ] (right bracket). Values are separated by , (comma).
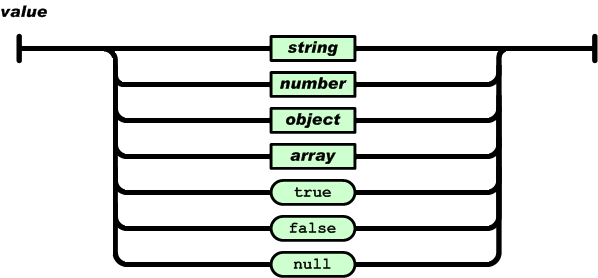
A value can be a string in double quotes, or a number, or true or false or null, or an object or an array. These structures can be nested.
Lets learn how to use JSON with Java. Here are some sample JAVA examples:
Here is a sample JSONArray which contains more than one JSONObjects.
[
{
color: "red",
value: "#f00"
},
{
color: "green",
value: "#0f0"
},
{
color: "blue",
value: "#00f"
},
{
color: "cyan",
value: "#0ff"
},
{
color: "magenta",
value: "#f0f"
},
{
color: "yellow",
value: "#ff0"
},
{
color: "black",
value: "#000"
}
]
File: https://crunchify.com/wp-content/uploads/code/jsonArray.txt
You can download json.jar from here: http://json-lib.sourceforge.net/
Put it under your eclipse project’s lib folder and include it as project build path dependency. In next post I’ll explain some Java examples which manipulates JSONObjects and JSONArray.

