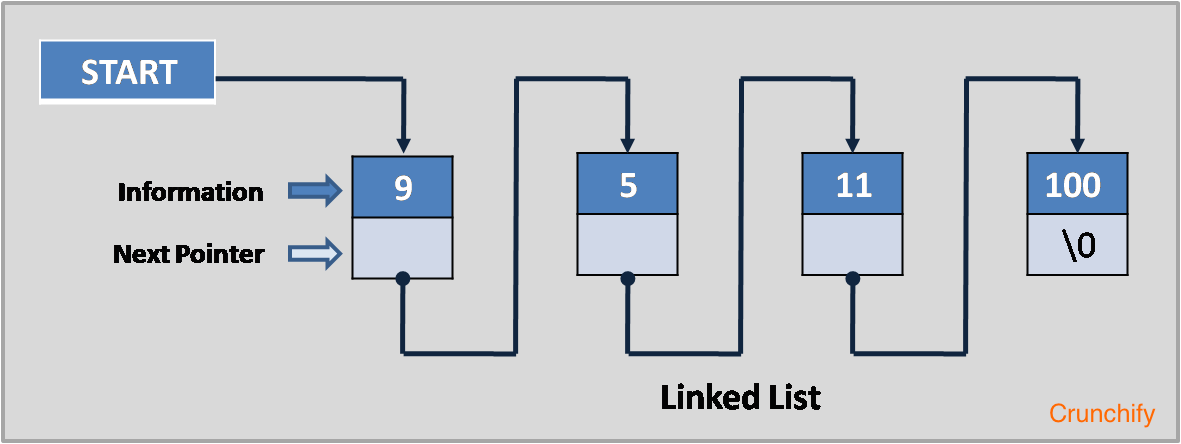
A linked list is a data structure that consists of a sequence of nodes, where each node contains an element and a reference to the next node. In this post, we will see how to find the middle element of a linked list in Java.
There are two approaches to finding the middle element of a linked list in Java:
- Using two pointers
- Using the size of the linked list
Let’s take a look at each approach in detail.
Method 1: Using Two Pointers
In this approach, we use two pointers, slow and fast, where slow moves one step at a time and fast moves two steps at a time. This way, when fast reaches the end of the linked list, slow will be at the middle of the linked list.
Here’s the implementation of this approach:
package crunchify.com.java.tutorials;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* @author Crunchify
* Finding the Middle Element of a Linked List in Java.
*/
public class CrunchifyLinkedListMiddleElement {
public static Integer findMiddleElement(LinkedList<Integer> crunchifyLinkedList) {
if (crunchifyLinkedList.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
CrunchifyListNode slow = crunchifyLinkedList.getFirst();
CrunchifyListNode fast = crunchifyLinkedList.getFirst();
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
return slow.data;
}
private static class CrunchifyListNode {
int data;
CrunchifyListNode next;
CrunchifyListNode(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList<Integer> cruchifyList = new LinkedList<>();
cruchifyList.add(1);
cruchifyList.add(2);
cruchifyList.add(3);
cruchifyList.add(4);
cruchifyList.add(5);
Integer middleElement = findMiddleElement(cruchifyList);
System.out.println("Middle element of linked list: " + middleElement);
}
}
Just run above program as a Java Application and you will see result as below.
Middle element of linked list: 3 Process finished with exit code 0
Method 2: Using the Size of the Linked List
Another approach to finding the middle element of a linked list is to determine the size of the linked list, then traverse the linked list to reach the middle element. This method involves iterating through the linked list to find its size, and then using that size to determine the middle element.
Here’s an example implementation of this approach. Below is the simplest way to find Middle Element of LinkedList:
package com.crunchify.tutorials;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author Crunchify
* Finding the Middle Element of a Linked List in Java.
*/
public class CrunchifyFindMiddleInLinkedList {
/**
* @author Crunchify.com
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
list.add(String.valueOf(i));
}
System.out.println("Middle Element of Linked List is: " + FindMiddle1(list));
}
private static String FindMiddle1(List<String> list) {
int size = list.size();
int middle = (size / 2);
return list.get(middle).toString();
}
}
Output:
Middle Element of Linked List is: 50
Let me know if you face any issue running this program.
