Java Collection Framework is one of the most used section. There are more than 100 APIs are available for us to use at fingertips.
synchronizedMap() returns a synchronized (thread-safe) map backed by the specified map and we will use one more API synchronizedList().
If you have any of below questions then you are at right place:
- Get Synchronized List from ArrayList example
- How do I synchronize a collection?
- How do I synchronize a List or other Collection in Java
- Collections.synchronizedList and synchronized
- java.util.Collections.synchronizedMap() Method Example
- Java Thread Synchronization Tutorial
In this Java example I’ll show how to Synchronized Map and List. We will be using synchronizedMap() method is used to return a synchronized (thread-safe) map backed by the specified map and the same way synchronizedList().
Let’s use List in description. The Collections class provides us with synchronizedList(List list) API method, that returns a synchronized (thread-safe) list from the provided ArrayList.
Here are the detailed Steps:
- Create an ArrayList
- Populate the arrayList with elements, with add(E e) API method of ArrayList
- Invoke the synchronizedList(List list) API method of Collections to get the synchronized list from the provided ArrayList
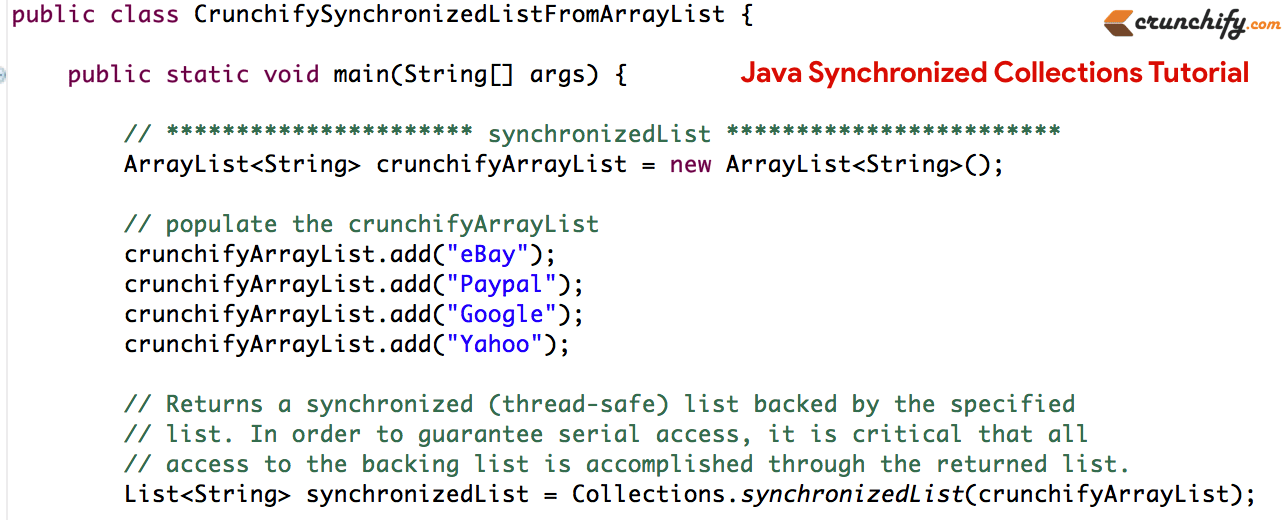
Let’s take a look at the code snippet:
package com.crunchify.tutorials;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author Crunchify.com
*
*/
public class CrunchifySynchronizedListFromArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ********************** synchronizedList ************************
ArrayList<String> crunchifyArrayList = new ArrayList<String>();
// populate the crunchifyArrayList
crunchifyArrayList.add("eBay");
crunchifyArrayList.add("Paypal");
crunchifyArrayList.add("Google");
crunchifyArrayList.add("Yahoo");
// Returns a synchronized (thread-safe) list backed by the specified
// list. In order to guarantee serial access, it is critical that all
// access to the backing list is accomplished through the returned list.
List<String> synchronizedList = Collections.synchronizedList(crunchifyArrayList);
System.out.println("synchronizedList conatins : " + synchronizedList);
// ********************** synchronizedMap ************************
Map<String, String> crunchifyMap = new HashMap<String, String>();
// populate the crunchifyMap
crunchifyMap.put("1", "eBay");
crunchifyMap.put("2", "Paypal");
crunchifyMap.put("3", "Google");
crunchifyMap.put("4", "Yahoo");
// create a synchronized map
Map<String, String> synchronizedMap = Collections.synchronizedMap(crunchifyMap);
System.out.println("synchronizedMap contains : " + synchronizedMap);
}
}
Eclipse Console Result:
synchronizedList conatins : [eBay, Paypal, Google, Yahoo]
synchronizedMap contains : {3=Google, 2=Paypal, 1=eBay, 4=Yahoo}
