Learn how to efficiently reverse a singly LinkedList in Java using the CrunchifyReverseLinkedList program from Crunchify.com. This Java program demonstrates a straightforward approach to reversing the order of elements within a LinkedList, including methods to add and iterate through elements. Enhance your Java programming skills with this educational tutorial.
Reverse Singly Linked List is one of the best all time favorite interview question for me. I remember asking the same questions to interviewer in different way.
In this tutorial we will go over simple way to reverse Linked List in Java. This defines generic singly linked list class and demonstrates its usage by creating a linked list of integers, adding elements to it, reversing the list, and then printing the original and reversed linked lists. It serves as a basic example of working with linked lists and reversing them in Java.
Here is a complete Java program logic
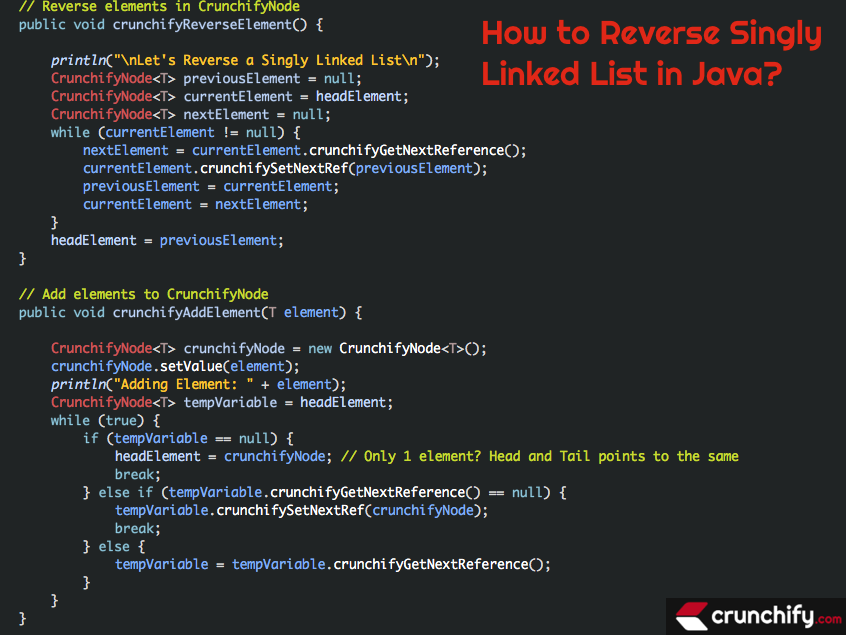
The reversal of a singly linked list using a generic class called CrunchifyReverseLinkedList.
Let’s go through the code step by step:
- The code is organized into a Java package named
crunchify.com.tutorial. - The class
CrunchifyReverseLinkedListis parameterized with a generic typeTto allow flexibility in the data types that the linked list can hold. - Inside the class, there’s a private instance variable
headElementof typeCrunchifyNode<T>. This will serve as the head (start) of the linked list. - The class defines several methods:
crunchifyIterateElement(): This method iterates through the linked list and prints its elements using a temporary variable to traverse the list.crunchifyReverseElement(): This method reverses the linked list by changing the pointers/references of the nodes. It uses three temporary variables:previousElement,currentElement, andnextElementto reverse the pointers.crunchifyAddElement(T element): This method adds elements to the linked list. It creates a newCrunchifyNodeinstance, sets its value, and adds it to the end of the linked list.
- The
mainmethod is used for testing. It creates an instance ofCrunchifyReverseLinkedListparameterized withIntegertype. - In the
mainmethod:- A random number generator is used to generate 8 random integers between 21 and 54 (inclusive) and adds them to the linked list.
- The original linked list is printed using
crunchifyIterateElement(). - The linked list is then reversed using
crunchifyReverseElement(). - The reversed linked list is printed again using
crunchifyIterateElement().
- The utility methods
printlnandprintare used for simple logging with newline and without newline, respectively.
Let’s get started:
- Create
CrunchifyNodeclass withcrunchifyNodeValueandnodeNextReferenceobject - Create getter() and setter() methods for the same
- We will override compareTo() method as per our need
- Create class
CrunchifyReverseLinkedList.java - Add 3 methods for different operations
- crunchifyAddElement()
- crunchifyIterateElement()
- crunchifyReverseElement()
- main() method
- First create a Linked List. Add 8 elements to it.
- Iterate through a list and print
- Reverse a list
- Iterate through it again and print
Here is a complete Java Code:
CrunchifyReverseLinkedList.java
package crunchify.com.tutorial;
/**
* @author Crunchify.com
* Program: Best way to reverse Singly LinkedList in
* Java Version: 1.0.2
*
*/
public class CrunchifyReverseLinkedList<T> {
private CrunchifyNode<T> headElement;
// Iterate through elements in CrunchifyNode
public void crunchifyIterateElement() {
CrunchifyNode<T> tempVariable = headElement;
while (true) {
if (tempVariable == null) {
break;
}
print(tempVariable.getValue() + " ");
tempVariable = tempVariable.crunchifyGetNextReference();
}
}
// Reverse elements in CrunchifyNode
public void crunchifyReverseElement() {
println("\nReversing Linked List now...\n");
CrunchifyNode<T> previousElement = null;
CrunchifyNode<T> currentElement = headElement;
CrunchifyNode<T> nextElement = null;
while (currentElement != null) {
nextElement = currentElement.crunchifyGetNextReference();
currentElement.crunchifySetNextRef(previousElement);
previousElement = currentElement;
currentElement = nextElement;
}
headElement = previousElement;
}
// Add elements to CrunchifyNode
public void crunchifyAddElement(T element) {
CrunchifyNode<T> crunchifyNode = new CrunchifyNode<T>();
crunchifyNode.setValue(element);
println("Adding Element: " + element);
CrunchifyNode<T> tempVariable = headElement;
while (true) {
if (tempVariable == null) {
headElement = crunchifyNode; // Only 1 element? Head and Tail points to the same
break;
} else if (tempVariable.crunchifyGetNextReference() == null) {
tempVariable.crunchifySetNextRef(crunchifyNode);
break;
} else {
tempVariable = tempVariable.crunchifyGetNextReference();
}
}
}
// Main Method for Testing
public static void main(String a[]) {
CrunchifyReverseLinkedList<Integer> crunchifyLinkedList = new CrunchifyReverseLinkedList<Integer>();
int crunchifyRandomNo;
println("in main()...\n");
// Let's create integer array with 15 values in it
for (int i = 1; i <= 8; i++) {
crunchifyRandomNo = (21 + (int) (Math.random() * ((55 - 2)))); // We are just getting total 8 Random elements
crunchifyLinkedList.crunchifyAddElement(crunchifyRandomNo);
}
println("\nOriginal Linked List:");
crunchifyLinkedList.crunchifyIterateElement();
println("");
crunchifyLinkedList.crunchifyReverseElement();
println("Reversed Linked List:");
crunchifyLinkedList.crunchifyIterateElement();
}
// Simple Log utility with new line
private static void println(String string) {
System.out.println(string);
}
// Simple Log utility
private static void print(String string) {
System.out.print(string);
}
}
CrunchifyNode.java
package crunchify.com.tutorial;
/**
* @author Crunchify.com
* Program: Crunchify Node Element
* Version: 1.0.0
*
*/
public class CrunchifyNode<T> implements Comparable<T> {
private T crunchifyNodeValue;
private CrunchifyNode<T> nodeNextReference;
public T getValue() {
return crunchifyNodeValue;
}
public void setValue(T nodeValue) {
this.crunchifyNodeValue = nodeValue;
}
public CrunchifyNode<T> crunchifyGetNextReference() {
return nodeNextReference;
}
public void crunchifySetNextRef(CrunchifyNode<T> nodeNextReference) {
this.nodeNextReference = nodeNextReference;
}
// @Override indicates that a method declaration is intended to override a method declaration in a supertype.
@Override
public int compareTo(T nodeValue) {
if (nodeValue == this.crunchifyNodeValue) {
return 0;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
}
Run a Java program in Eclipse IDE
Check out result. Here is an Eclipse Console result.
in main()... Adding Element: 49 Adding Element: 41 Adding Element: 21 Adding Element: 43 Adding Element: 45 Adding Element: 56 Adding Element: 40 Adding Element: 63 Original Linked List: 49 41 21 43 45 56 40 63 Reversing Linked List now... Reversed Linked List: 63 40 56 45 43 21 41 49
Here is a full program as a image for your reference.
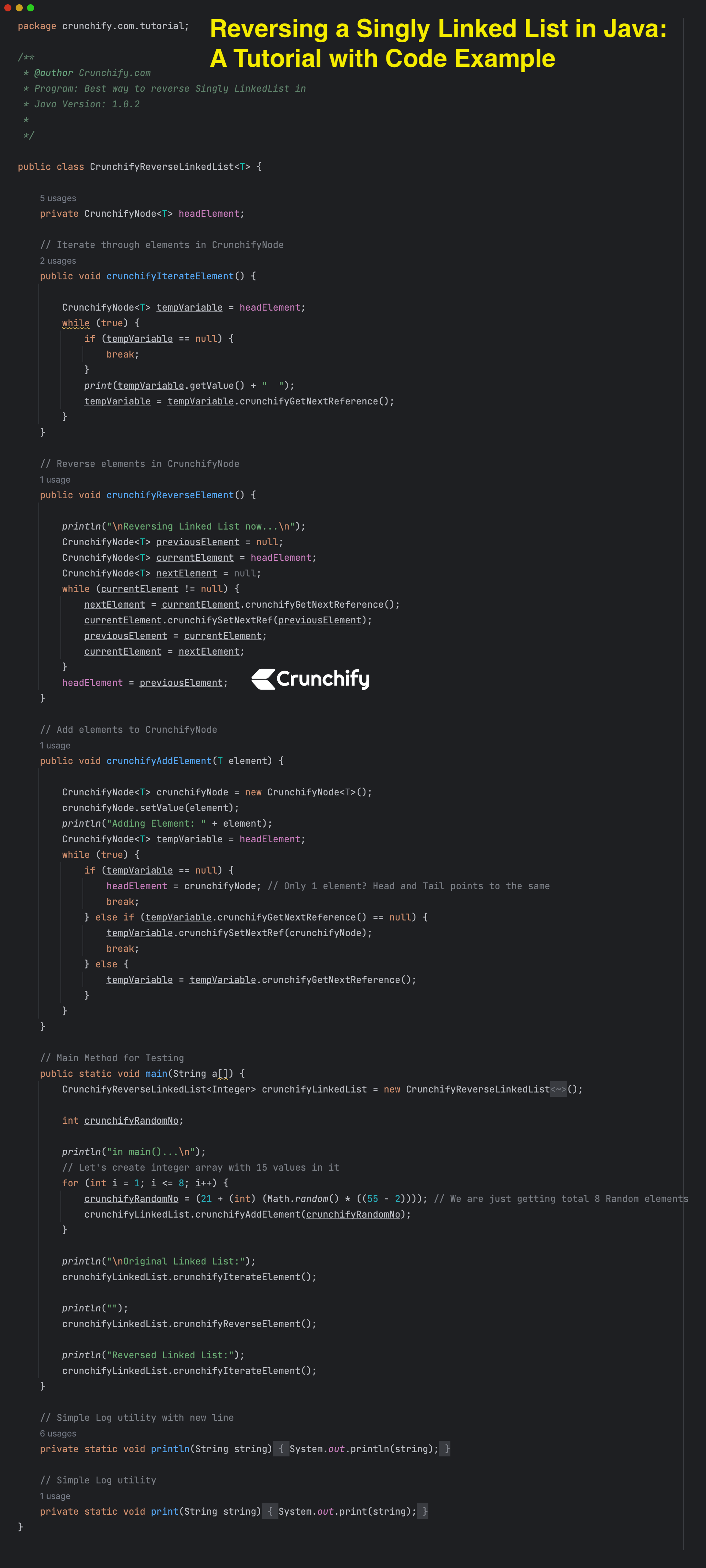
Hope you get a complete picture on how to reverse a Singly LinkedList in Java in best simple way. Let me know if you have any questions.
